Discover how blockchain consensus and layers work, their powerful benefits, and hidden risks. Learn the essentials for secure, scalable digital innovation.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Blockchain has transformed how we think about trust, transactions, and digital ownership. From powering Bitcoin to enabling decentralized finance (DeFi), blockchain technology relies on consensus mechanisms and layered architecture to function. Yet, behind the hype lies both powerful benefits and hidden risks that businesses, developers, and investors must understand.
In this guide, we’ll explain blockchain consensus and layers in simple terms, explore real-world benefits, and reveal challenges that are often overlooked.
1. What Is Blockchain Consensus?

Consensus is the process by which blockchain networks agree on the state of data. Since there’s no central authority, participants (nodes) must collectively validate transactions.
Popular Consensus Mechanisms
Proof of Work (PoW): Used by Bitcoin, it secures the network through mining power.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators are chosen based on coin holdings, as seen in Ethereum 2.0.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): Used by EOS, relies on elected validators for faster performance.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT): Ensures security even if some nodes act maliciously.
Each method has trade-offs between security, scalability, and decentralization, the blockchain trilemma.
2. The Layered Architecture of Blockchain
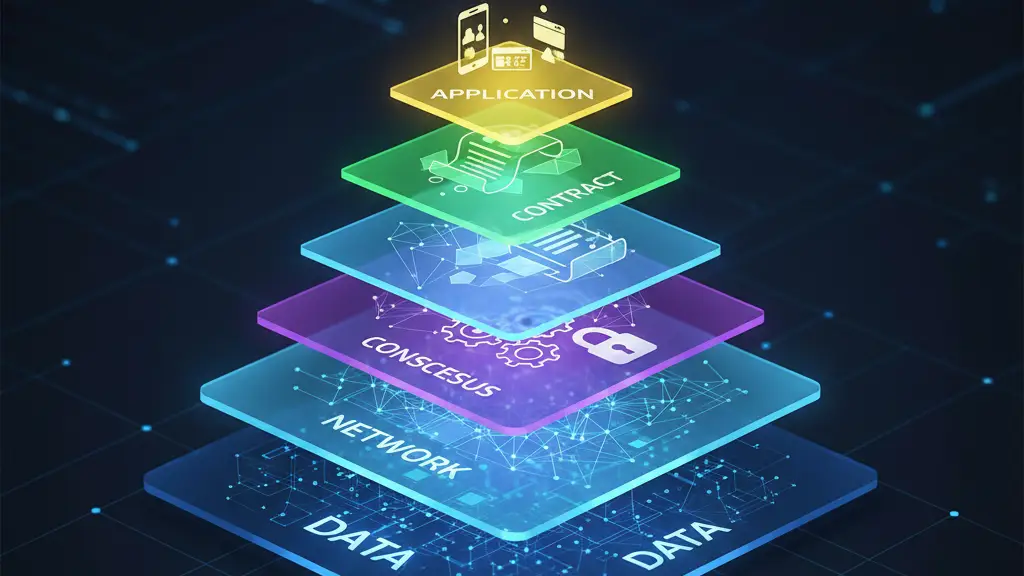
Blockchain isn’t a single block of code, it’s a stack of layers working together.
Main Blockchain Layers
Data Layer: Stores blocks, transactions, and cryptographic hashes.
Network Layer: Handles peer-to-peer communication between nodes.
Consensus Layer: Ensures agreement on transaction validity.
Contract Layer: Executes smart contracts and business logic.
Application Layer: Provides user-facing applications (DeFi, NFTs, supply chain apps).
This layered design makes blockchain modular, scalable, and flexible, but also creates new attack points.
3. Benefits of Blockchain Consensus

Consensus ensures that blockchain systems deliver trust without intermediaries.
Key Benefits:
Security: Immutable and tamper-resistant data.
Transparency: Public verification of transactions.
Decentralization: No single point of control or failure.
Efficiency: Automated validation without middlemen.
Case Study: In 2021, Walmart used blockchain to track food safety in supply chains, cutting traceability time from 7 days to 2.2 seconds (source: Forbes).
4. Hidden Risks of Consensus

While consensus powers blockchain, it isn’t risk-free.
Risks include:
51% Attacks: If a group controls most of the network power, they can manipulate transactions.
Energy Consumption: PoW networks consume as much electricity as small countries.
Centralization Risks: PoS may give too much power to wealthy stakeholders.
Latency Issues: Some consensus mechanisms slow down transaction speeds.
Example: Ethereum’s shift from PoW to PoS reduced energy use by 99.95%, but debates continue about validator centralization.
5. How Blockchain Layers Improve Scalability

Blockchain layers solve performance bottlenecks by separating functions.
Layer 1 (Base chain): Core blockchain like Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Layer 2 (Scaling solutions): Lightning Network, Polygon, and rollups improve speed.
Cross-Chain Bridges: Connect different blockchains for interoperability.
Without layered scaling, blockchain adoption in banking, supply chain, and gaming would remain limited.
6. Use Cases: Real-World Power of Blockchain

Blockchain consensus and layers enable disruptive applications:
Finance (DeFi): Lending, staking, and trading without banks.
Healthcare: Secure patient data exchange across institutions.
Voting Systems: Tamper-proof digital elections.
NFTs & Metaverse: Ownership of digital assets.
Supply Chain: End-to-end product tracking.
Example: Estonia uses blockchain-based systems to secure national healthcare records.
7. Future of Blockchain Consensus & Layers

Experts believe blockchain will evolve into a multi-layered, interoperable ecosystem.
Predictions:
Hybrid Consensus: Combining PoW, PoS, and BFT for balance.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Boosting privacy and scalability.
Post-Quantum Cryptography: Preparing for future cyber threats.
Decentralized AI + Blockchain: Autonomous networks powered by machine learning.
The future lies in making blockchain faster, greener, and more inclusive.
8. FAQs
Q1: What is blockchain consensus in simple terms?
Consensus is how blockchain participants agree on which transactions are valid without a central authority.
Q2: Why are blockchain layers important?
Layers separate responsibilities, making blockchain more scalable, modular, and secure.
Q3: What are the risks of blockchain consensus?
Risks include 51% attacks, centralization in PoS, energy use in PoW, and slower transaction speeds.
Q4: Can blockchain replace traditional banking?
Not entirely yet, but blockchain is transforming payments, lending, and cross-border transactions.
Conclusion
Blockchain consensus and layered architecture are the backbone of decentralization. They bring transparency, trust, and efficiency—but also risks like energy costs and centralization.
As blockchain matures, businesses must balance benefits and hidden risks to unlock its full potential.
🚀 Ready to dive deeper? Explore our blog article in-depth deep guides on (Blockchain Fundamentals) to stay ahead in the blockchain revolution.


2 thoughts on “Blockchain Consensus & Layers Explained: 8 Powerful Benefits Vs Hidden Risks”