Discover blockchain fundamentals, how it works, key features, and real-world applications. A beginner’s guide to understanding this digital revolution.
Introduction
The world is rapidly shifting toward digital-first systems, and at the heart of this transformation lies blockchain fundamentals. From cryptocurrencies to supply chain tracking, blockchain is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a technology reshaping industries. But what exactly makes blockchain so powerful? Why is it considered the backbone of Web3, decentralized finance, and future governance models? In this guide, we’ll break down blockchain fundamentals in simple terms, so you can understand its working, applications, and future potential.
What is Blockchain? The Core of Trustless Systems

At its essence, blockchain is a decentralized, distributed digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Unlike traditional databases, no single authority owns or controls it.
Key characteristics of blockchain:
Decentralization: No central authority, meaning no single point of failure.
Immutability: Once data is added, it cannot be altered.
Transparency: Transactions are publicly verifiable.
Security: Cryptography ensures trust without intermediaries.
👉 Example: Bitcoin uses blockchain to enable peer-to-peer payments without banks. According to Investopedia, Wikipedia blockchain is the foundation of nearly all digital assets today.
How Blockchain Works Step by Step
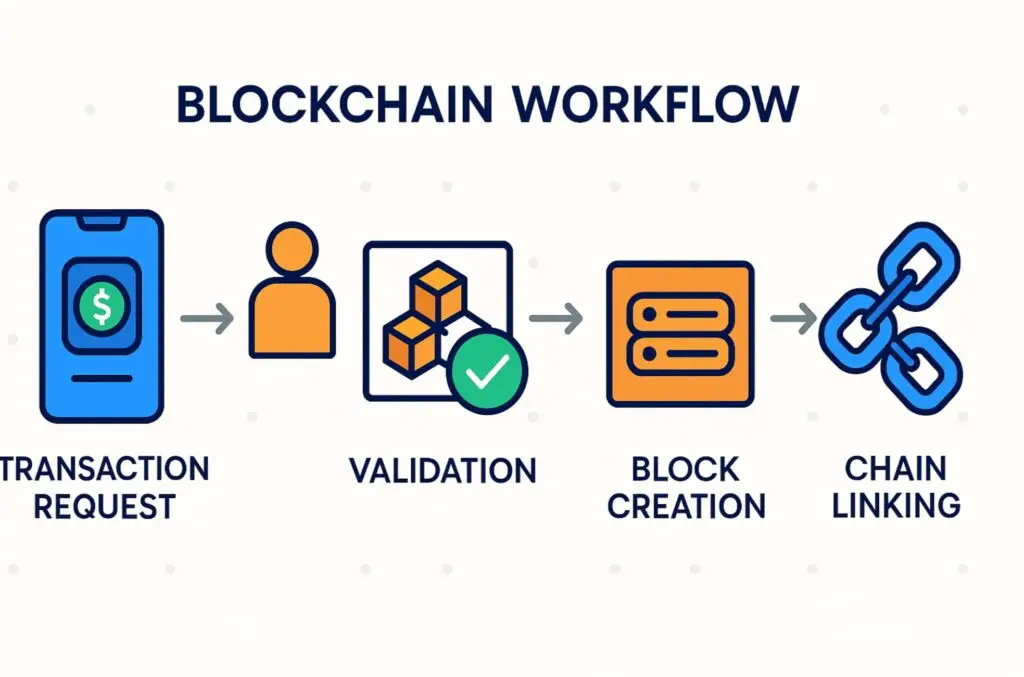
Understanding blockchain fundamentals requires knowing how blocks are added:
1. Transaction initiated – A user requests a transaction (payment, contract, or data exchange).
2. Validation – The transaction is verified by nodes (computers in the network).
3. Block creation – Verified transactions are grouped into a block.
4. Consensus mechanism – Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) ensures agreement across the network.
5. Block added to chain – The new block links to the previous one, forming an immutable chain.
6. Completion – The transaction is successfully executed and permanently recorded.
This step-by-step process ensures trust without intermediaries.
Types of Blockchain: Public, Private, Hybrid
Not all blockchains are the same. Based on control and usage, there are three main types:
Public Blockchain – Open to all (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum). Best for transparency.
Private Blockchain – Controlled by a single entity, often used in enterprises.
Hybrid Blockchain – Combines features of both public and private.
📌 Example: Walmart uses a private blockchain for supply chain management, while Ethereum powers DeFi through a public blockchain.
Key Features of Blockchain Technology

The popularity of blockchain stems from its unique features:
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) – Everyone in the network holds a copy.
Smart Contracts – Self-executing agreements with predefined rules.
Tokenization – Assets (real estate, art, stocks) can be represented digitally.
Consensus Mechanisms – Algorithms like PoW, PoS, and DPoS ensure trust.
💡 Fun Fact: According to Deloitte, more than 80% of companies are exploring blockchain integration.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain
Blockchain fundamentals go beyond crypto. Its real-world applications include:
Finance (DeFi) – Peer-to-peer lending, trading, and stablecoins.
Supply Chain – Track goods from production to delivery.
Healthcare – Secure patient data sharing.
Voting Systems – Transparent, tamper-proof digital voting.
NFTs – Unique ownership of digital assets.
👉 Example: The Ethereum blockchain has powered over $40B in NFT transactions.
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain
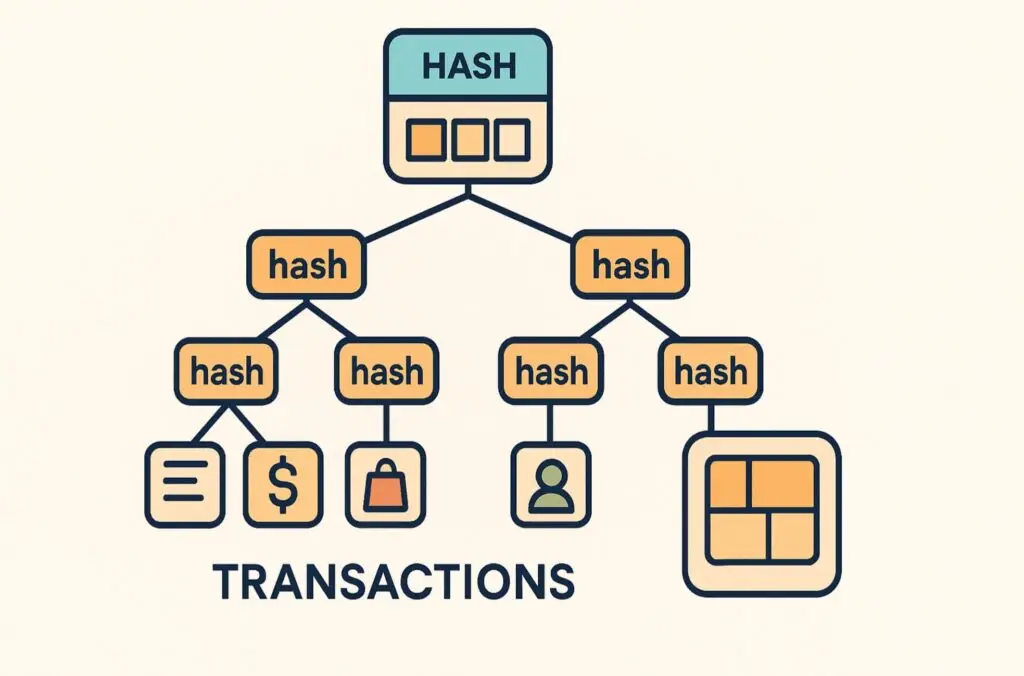
Like any technology, blockchain has pros and cons.
Benefits:
Eliminates intermediaries
Enhances security
Reduces costs
Increases transparency
Challenges:
Scalability issues (transactions per second)
High energy consumption in PoW
Regulatory uncertainty
User adoption barriers
🌍 Despite challenges, blockchain adoption continues to rise across industries.
Blockchain vs Traditional Databases
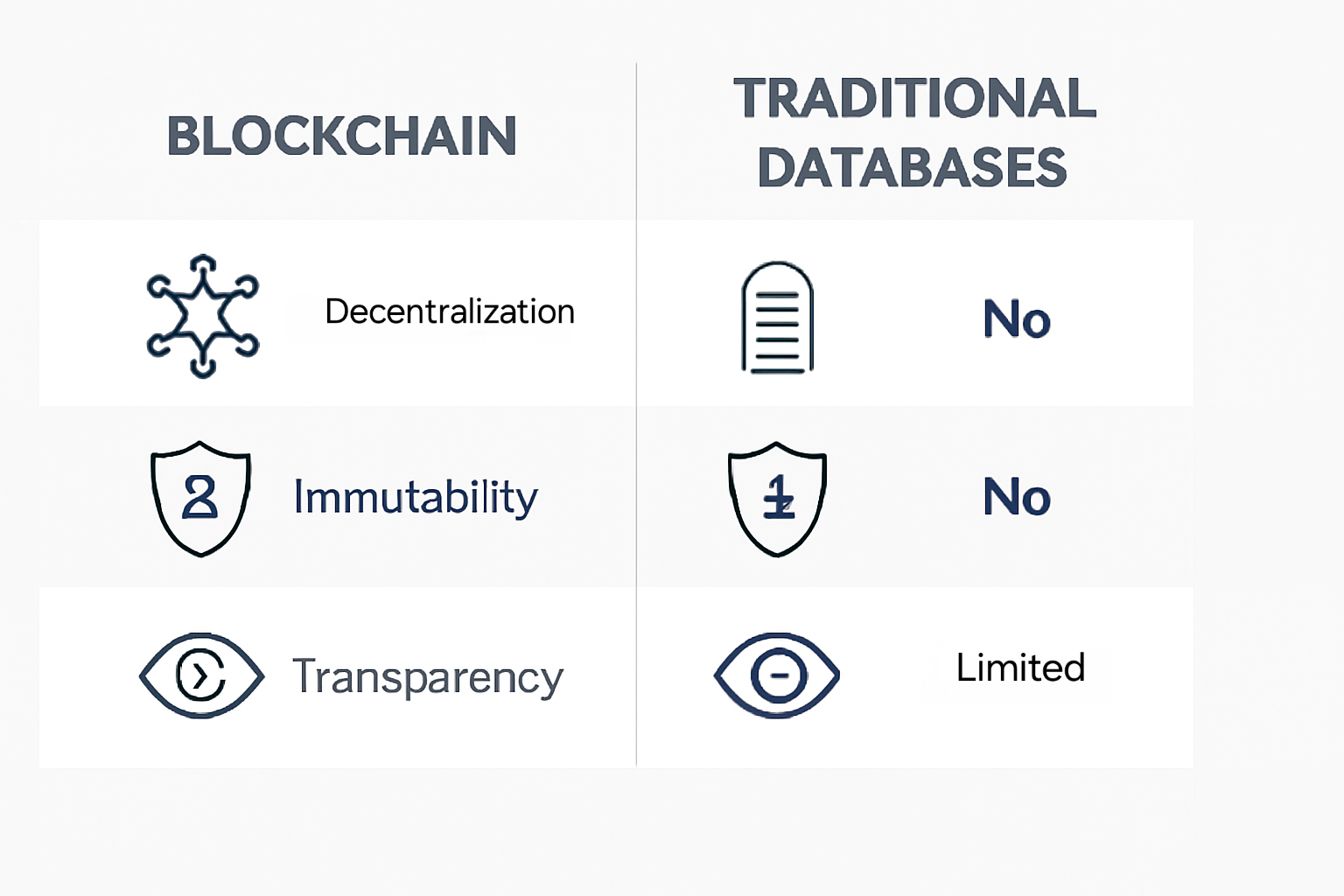
A common question in blockchain fundamentals: How does it differ from traditional databases?
Feature Blockchain Traditional Database
Control Decentralized Centralized
Data Modification Immutable Editable
Transparency Publicly verifiable Limited
Security Cryptography-based Password-based
📌 While databases excel in speed and efficiency, blockchain wins in trust and transparency.
The Future of Blockchain

The future of blockchain looks promising, with experts predicting:
Mass adoption of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Expansion of Web3 ecosystems
Integration with Artificial Intelligence and IoT
Mainstream NFT adoption in gaming, real estate, and media
According to Forbes, the blockchain industry is expected to surpass $1.4 trillion by 2030. The fundamentals we understand today will be the building blocks of tomorrow’s economy.
FAQs on Blockchain Fundamentals
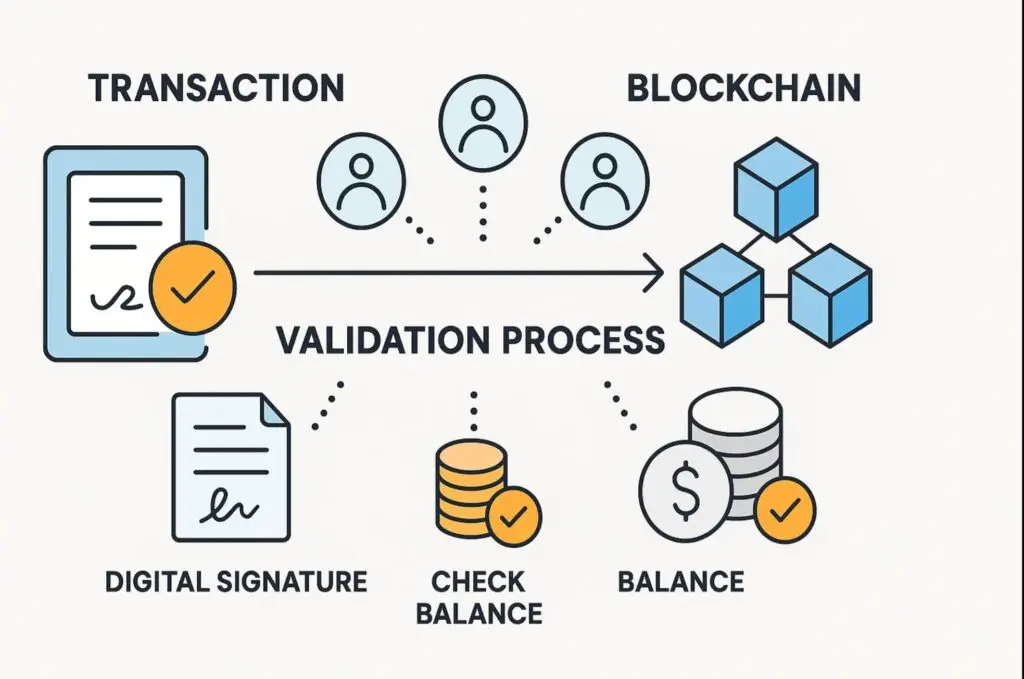
Q1. What are blockchain fundamentals in simple terms?
Blockchain fundamentals refer to the core concepts like decentralization, transparency, immutability, and cryptography that make blockchain work.
Q2. Why is blockchain better than traditional databases?
Unlike centralized databases, blockchain ensures transparency, immutability, and security without needing a middleman.
Q3. What industries use blockchain technology?
Finance, healthcare, supply chain, real estate, and entertainment industries widely adopt blockchain.
Q4. Is blockchain only about cryptocurrency?
No, while cryptocurrencies are popular, blockchain extends to smart contracts, NFTs, digital identity, and enterprise applications.
Conclusion
Understanding blockchain fundamentals is crucial for anyone looking to participate in the digital economy. From powering cryptocurrencies to transforming supply chains and healthcare, blockchain is redefining trust, transparency, and security in the modern world.
📢 Call to Action: If you’re serious about learning how blockchain can impact your career, investments, or business, explore our in-depth guides at FINOMILES. Stay ahead in the decentralized future!


3 thoughts on “Blockchain Fundamentals Made Simple in 2025: You Need To Know The Powerful Insights, No Confusion”